About This Report
This report is based on data collected by the National Council of Architectural Registration Boards (NCARB) during the 2023 calendar year, providing insight into the path to licensure.
NCARB maintains a database of licensure candidates and Certificate holders. This allows us to track the progression of candidates as they move through the AXP, ARE, and beyond.
Some of the data is self-reported, including age, race and ethnicity, gender, and geographic location. Other data is triggered by candidate actions, such as starting the AXP or completing the ARE. NCARB also collects data from the U.S. jurisdictional licensing boards to provide a total count of architects.
Data from the National Architectural Accrediting Board (NAAB) was also used in this report to provide the number of students entering and graduating from NAAB-accredited programs.
How to Read This Report
Here are some tips for understanding the data presented in NCARB by the Numbers.
Reading Charts
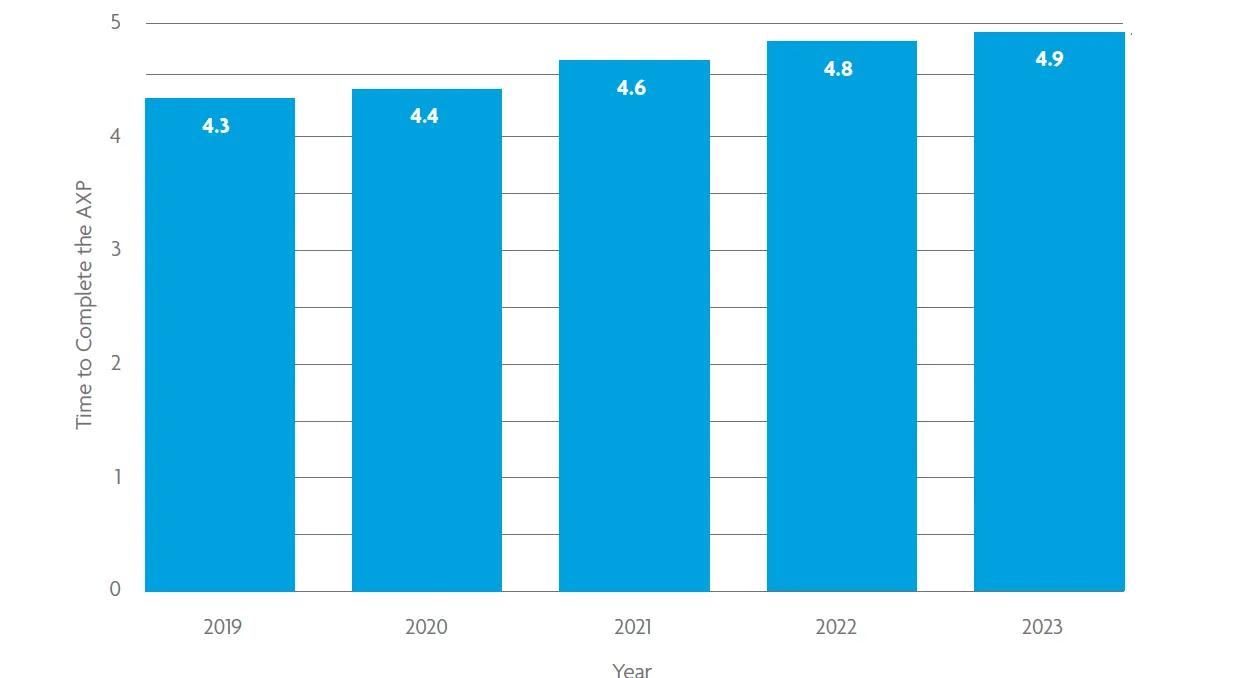
Most NCARB by the Numbers charts show a year-over-year comparison of data from NCARB’s Record holders. For example, each bar in the chart below shows the average time it took for candidates to complete the experience program in a given year.

The x (or horizontal) axis of this chart measures time in years, while the y (or vertical) axis measures the average time to complete the program in each individual year. Reading this chart, you can see the average licensure candidate who completed the AXP in 2023 took 4.9 years, a slight increase compared to 2022.
A note about averages: There are several ways to measure averages. NCARB typically uses the median, rather than mean. The median provides a more accurate measure for the types of data shown in NCARB by the Numbers, because it better accounts for outliers that skew the overall dataset (like a candidate who takes decades to complete a program).
Demographics
Throughout this year’s report, we segment NCARB Record holder data by a variety of demographic factors, such as race and ethnicity, gender, and age.
In the 2023 edition of NCARB by the Numbers, we adjusted the way we present data around racial and ethnic diversity to reflect the fact that individuals can identify as more than one race or ethnicity. For this reason, some demographic percentages may add to over 100%. In addition, NCARB launched updated demographics selections for Record holders in 2023, some of which are reflected in this year’s report.
Individuals who identify their race as either American Indian/Alaskan Native, Native Hawaiian/ Pacific Islander, or Middle Eastern or North African make up a fraction of all NCARB customers. For this reason, they are grouped into the individuals of “another group” category.
Additionally, NCARB recognizes that our community’s gender identity is more diverse than the “male” and “female” categories represented in NCARB by the Numbers and began collecting more comprehensive data on gender identity in 2023. However, due to an insufficient sample size of non-binary and gender non-conforming individuals, only data for male and female individuals are captured in this report.
Some new demographic fields—including those related to disability status, sexual orientation, and transgender status—have not been utilized by enough Record holders to include in this year’s edition of NCARB by the Numbers. We hope to report on these areas in future years.
Percentage Changes vs. Percentage Point Changes
Throughout the 2024 NCARB by the Numbers, we refer to changes in the data as either “percentage point changes” or “percent changes.” Percent change measures the rate of change from one number to another (i.e., going from 40,000 to 50,000 is a 25% increase). Percentage point changes, on the other hand, measure the numerical difference in percentages (i.e., going from 40 percent to 50 percent is an increase of 10 percentage points).
NCARB typically uses percentage point changes when comparing proportions of different cohorts or groups—for example, when comparing the racial and ethnic makeup of candidates who completed the AXP from 2023 to 2022. Because the number of candidates completing the AXP each year is different, referring to the change in percentage points rather than the change in percent change allows for a more accurate comparison of the proportion of candidates who identify as people of color each year.
NCARB is constantly updating how we filter and present data in NCARB by the Numbers to provide the most accurate information. If you have questions or comments about this year’s NCARB by the Numbers, please reach out to us at communications@ncarb.org.
Glossary
Age: Median age based on self-reported dates of birth.
Architect: An individual who is licensed to practice architecture by one of the 55 U.S. jurisdictions.
ARE: The Architect Registration Examination® (ARE®) is a multi-division exam used to assess a candidate’s knowledge and skills. It is required for initial licensure in all U.S. jurisdictions.
ARE/Exam Candidate: An NCARB Record holder who is currently taking the ARE.
ARE Completion: This data point is triggered when an exam candidate passes all ARE divisions.
AXP: The Architectural Experience Program® (AXP®) provides a framework to guide licensure candidates through earning and recording professional experience.
AXP Completion: This data point is triggered when a licensure candidate fulfills the AXP’s requirements, and their Record has been evaluated by NCARB.
Licensure Candidate: An NCARB Record holder who is actively documenting experience and/or taking the ARE.
NAAB: The National Architectural Accrediting Board (NAAB) accredits U.S. professional programs in architecture. All U.S. jurisdictions accept degrees from NAAB-accredited programs for initial licensure.
New Record: A candidate’s successful application for an NCARB Record, which is often the first step on the path to licensure.
NCARB Certificate: A credential available to architects that facilitates reciprocal licensure across U.S. jurisdictions, as well as Australia, Canada, Mexico, and New Zealand.
New Architect: NCARB does not receive reliable data regarding when a candidate first receives their license but estimates that a candidate becomes a new architect after becoming ready for licensure. “New Architects” includes candidates who became ready for licensure in the given year.
NOMA: The National Organization of Minority Architects.
Non-Certified Architect: An architect who does not hold an NCARB Certificate.
Pass Rate: Percentage of division attempts that received a passing score on an ARE division out of the total number of attempts on that division.
People of Color: Individuals who identified their race as American Indian or Alaskan Native; Asian; Black or African American; or Native Hawaiian or Pacific Islander, as well as individuals who indicated they were of Latino or Hispanic descent.
Ready for Licensure: The core requirements for licensure in the United States include gaining an education (typically a degree from a NAAB-accredited program), completing the AXP, and passing the ARE. Some jurisdictions have additional requirements that fall outside this “core,” such as a supplemental exam. NCARB considers a candidate ready for licensure when they have completed the core licensure requirements.
Reciprocal License: An architecture license issued by a jurisdiction as a result of the applicant holding an initial license in a separate jurisdiction.